

Company

Solutions

Knowledge&Blog

Contact Us
Posted by Qinghong
What Certifications Do Polyester Sterile PBT Bandages Require for Medical Use?
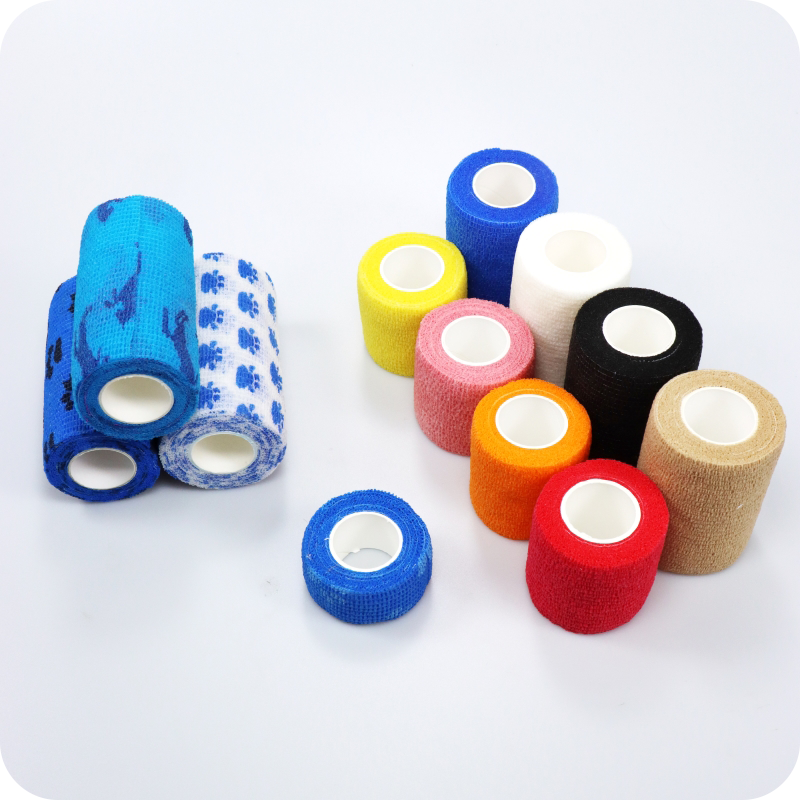
Polyester Sterile and non-sterile PBT Bandages are widely used in medical settings for wound care, offering a combination of strength, flexibility, and sterilization. However, to ensure that these bandages meet the necessary safety and performance standards, they must undergo various certifications.
Understanding Polyester Sterile and Non-Sterile PBT Bandages
Polyester Sterile and non-sterile PBT Bandages are commonly used in healthcare for a range of applications, including post-surgical wound care, burns, and abrasions. The distinction between sterile and non-sterile versions of these bandages is crucial to understanding their application and the necessary certifications.
- Polyester Sterile PBT Bandages are treated to be free of any living microorganisms and are essential for use in critical medical procedures where contamination is a major concern.
- Polyester Non-Sterile PBT Bandages, while effective, are used in less critical environments and must be sterilized before use if required.
Both types, however, must adhere to strict certification standards to ensure their safety and effectiveness.
Key Certifications for Medical Use
-
ISO 13485: Medical Devices - Quality Management Systems
- This certification outlines the requirements for a comprehensive quality management system for the design and manufacture of medical devices. It ensures that manufacturers consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- Polyester Sterile and non-sterile PBT Bandages that receive ISO 13485 certification demonstrate adherence to stringent quality control measures, ensuring that the products are safe and reliable for medical use.
-
CE Marking (Conformité Européenne)
- For European Union markets, the CE marking is essential for medical devices. It signifies that the product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection requirements.
- Polyester Sterile and non-sterile PBT Bandages with the CE mark are approved for use within the European Union, ensuring that they have undergone rigorous testing for safety and performance.
-
FDA Approval (Food and Drug Administration)
- In the United States, the FDA regulates medical devices and requires manufacturers to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of their products.
- Polyester Sterile and non-sterile PBT Bandages must meet FDA standards for medical use. This includes clinical trials, product testing, and proper documentation to ensure the bandages do not pose any risk to patients.
-
ISO 10993: Biocompatibility Evaluation of Medical Devices
- This certification ensures that the materials used in medical devices, such as Polyester Sterile and non-sterile PBT Bandages, do not cause harm when they come into contact with body tissues.
- Biocompatibility testing is crucial for these bandages to ensure they are safe for prolonged use on human skin.
The Importance of Certification in Medical Applications
Certifications ensure that Polyester Sterile and non-sterile PBT Bandages meet regulatory standards, safeguarding both healthcare providers and patients. These certifications help in:
- Reducing Risk: Proper certification reduces the risk of infection and complications associated with improperly manufactured medical devices.
- Ensuring Quality: Regular audits and quality control practices mandated by these certifications ensure that every batch of Polyester Sterile and non-sterile PBT Bandages meets the highest quality standards.
- Building Trust: Certified products are more likely to be trusted by healthcare professionals and patients, leading to widespread adoption.
Comparison of Certification Requirements for Polyester Sterile and Non-Sterile PBT Bandages
| Certification Type | Polyester Sterile PBT Bandages | Polyester Non-Sterile PBT Bandages |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 13485 | Required | Required |
| CE Marking | Required for European markets | Required for European markets |
| FDA Approval | Required for U.S. markets | Required for U.S. markets |
| ISO 10993 | Required | Required |
Testing and Compliance for Medical-Grade Bandages
For any Polyester Sterile and non-sterile PBT Bandages to be used in medical settings, they must undergo rigorous testing to comply with the necessary standards.
- Sterilization Testing: Sterile bandages must undergo validation processes to ensure that they are free from contaminants. This testing ensures that the sterilization process was effective, and the product remains safe until used.
- Strength and Durability Testing: Polyester Sterile and non-sterile PBT Bandages must be tested for tensile strength, flexibility, and overall durability to ensure they provide adequate support and protection to the wound.
- Skin Irritation Testing: To meet biocompatibility standards, the bandages must be tested to ensure they do not cause irritation or adverse reactions when in contact with human skin.
What Happens if Polyester Sterile PBT Bandages Fail to Meet Certification Requirements?
If Polyester Sterile and non-sterile PBT Bandages fail to meet the required certifications, several issues can arise:
- Recalls: Non-compliant products may be subject to market recalls, which can cause harm to the brand and result in financial and reputational losses.
- Legal and Regulatory Action: Failure to meet certification requirements can result in legal penalties and restrictions from regulatory authorities.
- Compromised Patient Safety: The primary risk of non-certified bandages is that they may not meet safety standards, increasing the risk of infection or allergic reactions in patients.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
What is the difference between sterile and non-sterile polyester pbt bandages?
- Sterile bandages are treated to be free of bacteria and other pathogens, while non-sterile bandages may require sterilization before use in critical environments.
-
How long are polyester sterile pbt bandages effective after sterilization?
- The effectiveness of sterilization is typically guaranteed until the expiry date, which can range from one to three years, depending on packaging.
-
Can polyester non-sterile pbt bandages be used in surgical settings?
- Non-sterile bandages can be used if sterilized before application. However, sterile bandages are preferred in surgical settings to minimize infection risks.
References
- ISO 13485: Medical Devices – Quality Management Systems
- CE Marking – European Union Health and Safety Regulations
- FDA Guidelines for Medical Devices
NEWS










 English
English  русский
русский  Français
Français  Español
Español  عربى
عربى 





 ENG
ENG

